| Have you found an error or do you want to add more
information to these pages? You can contact me at the bottom of the home page. |
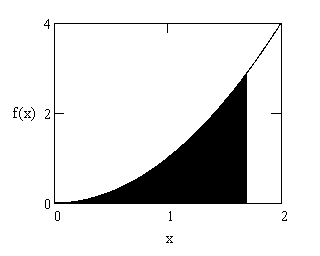
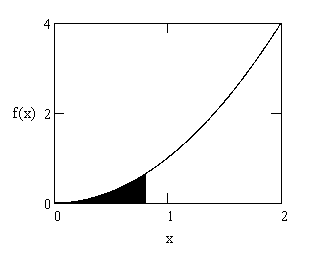
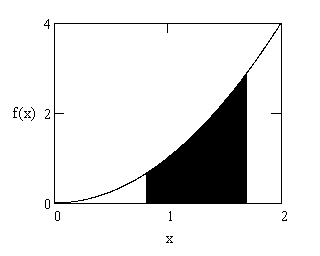
| ∫ | b | f(x) dx |
| a |
| ∫ |
dx x |
= | ∫ | 1 x | dx |
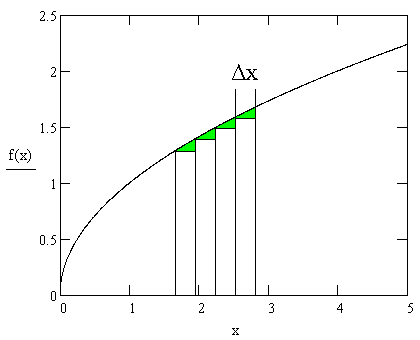
| lim | ∑ | yi•Δx | This just means a sum all the y values times Δx (a sum of all the areas of the rectangles) |
| Δx → 0 |
| = | ∫ | b | y dx Now this is not an approximation. It is like the above but with unimaginally small rectangles |
| a |
| [2x] | 10 2 |



|
minus |  |
equals |  |
| ∫ | 10 | 2 dt |
| 2 |
| = [2t + C] | 10 2 |
| d dx |
2x = 2 then ∫ 2 dx = 2x + C |
| d dx |
x | 2 | = 2x but also | d dx | x | 2 | + 5 = 2x |
| - | 1 R |
ln(E-Ri) = | t L | + C |
| - | 1 R |
ln(E-R0) = | 0 L | + C |
| - | 1 R |
ln(E) = | C |
| Have you found an error or do you want to add more
information to these pages? You can contact me at the bottom of the home page. |